LeetCode每日一题,117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
先看题目描述
大意就是给定一棵二叉树,让我们把里面每个节点的 next 指针指向其右侧的第一个节点
算法思路
BFS
由于这道题要的是把二叉树的每一行都串联起来,那么使用 BFS 来进行层次遍历就很合适,在遍历每一层时,让前一个节点的 next 指针指向当前节点即可
DFS
使用 DFS 来进行先根遍历,中根遍历或后根遍历都可以,只要保证是先遍历的左子树再遍历右子树就行,使用一个 HashMap 来存储当前遍历的某个深度对应的最右节点,在遍历到某个节点时,若 HashMap 的 key 中不存在当前深度,那么这个节点就是该深度的最左节点,将深度和该节点作为键值对添加到 HashMap 中;若 HashMap 的 key 中存在当前深度,那么此时该 key 值对应的 value 就是目前该深度的最右节点,令这个节点的 next 指针指向当前遍历的节点,再将该 key 值对应的 value 置为当前遍历的节点。遍历完后返回 root 即可
迭代
我们可以把每一行都看成一个链表,我们设置个 cur 看作是当前层的链表,设置个哑节点 flag 作为下一层的链表头,通过遍历当前层链表的节点来将下一层串联起来。将下一层串联成一个链表后,将 flag.next 赋值给 cur,后续继续遍历循环,直到 cur 为空为止。迭代完后返回 root 即可
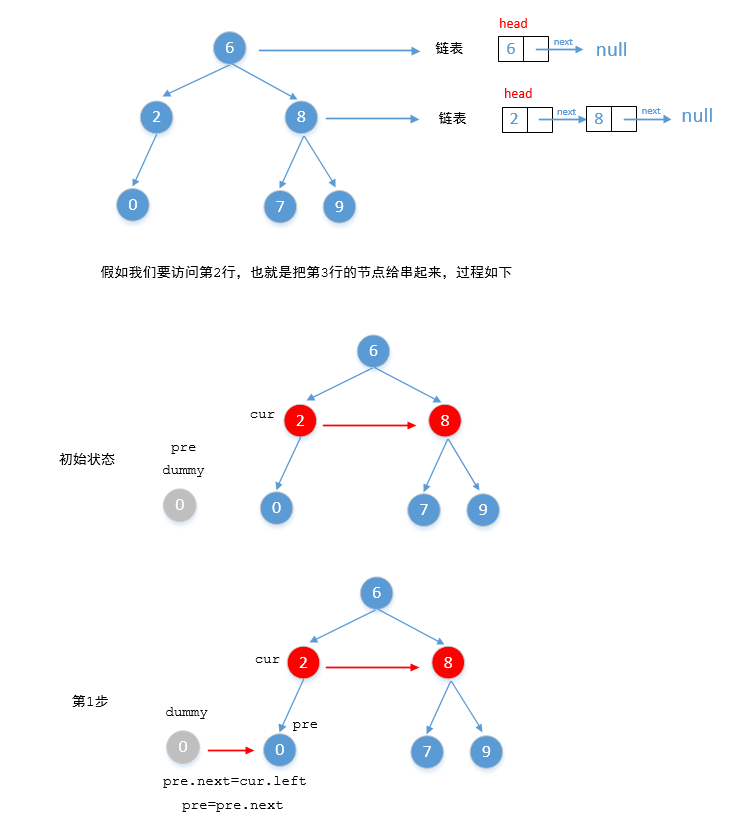
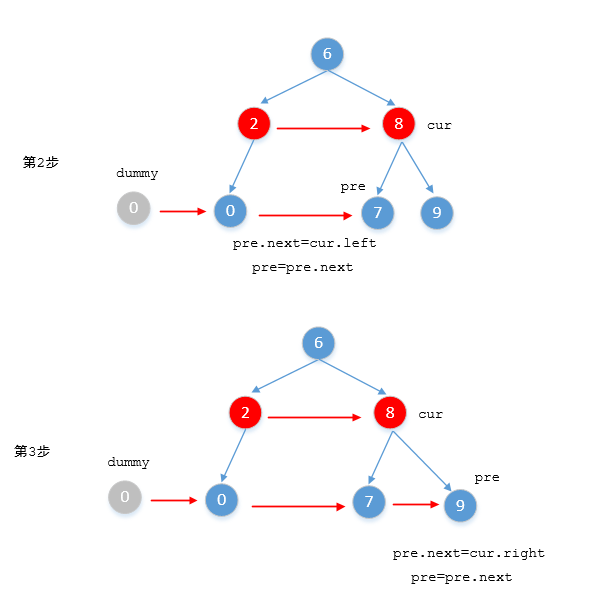
算法思路
BFS
1 | /* |
DFS
1 | /* |
迭代
1 | /* |